The Case
A five year old was jumping ever so vigorously in a bounce house and was knocked out of the bounce house by, as she noted, a “very big kid.” She landed awkwardly on her right shoulder and arm and cried out in immediate pain. She has no numbness and tingling in her hand, but “a whole lot” of pain in her upper arm. There are no lacerations or breaks in the skin. She was transported to the ED and the after some intranasal pain meds the following X-Ray was obtained (images courtesy Radiopedia):
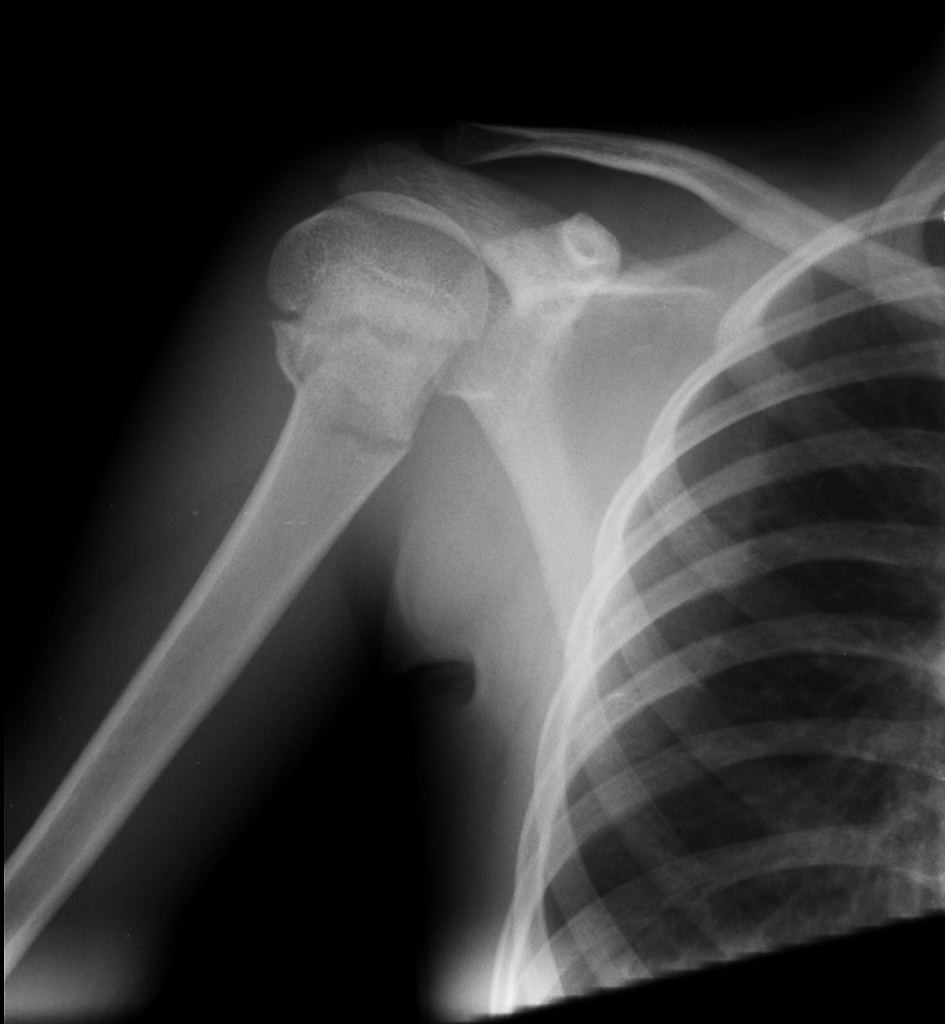
The Diagnosis
This is a transverse fracture of the proximal humerus – the so-called “surgical neck” of the humerus.
Management
Given that she has no neuromuscular deficits the management is conservative and includes placing her initially into a bulky splint + sling and swathe for comfort. You’ve got a few options- none is better than any other and your choice depends on patient comfort, size, and ability to manage it at home. From Academic Life in Emergency Medicine, below are some pictures of a couple of options. In addition to the two below I’ve also used a posterior long arm, and an upper arm sugartong nested together. Ultimately, the management is non-surgical in the vast majority of cases, and patients should be seen in Orthopedics with 3-5 days.
Either sling + swathe + splint or a shoulder immobilizer are recommended for minimally displaced fractures (≤ ⅓ the width of the shaft and ≤20 degrees angulated). Patients can start pendulum exercises in 2 to 4 weeks, then active range of motion movements including raising the arm overhead in 4 to 6 weeks. Return to usual activities is possible at 8 weeks. This patient was angulated, and therefore the splints seen below are recommended. Nevertheless almost all cases in this age range will remodel – without surgery – which is remarkable! Sometimes Ortho will place a hanging arm cast to add weight and can improve the deformity. Ibuprofen is the mainstay of pain management. Kids may want to sleep in a recliner for the first 1 to 2 weeks.
Kids ≥12 years with significant displacement generally get surgery. Anyone with an intra-articular fracture, dislocation + fracture, open fracture, or neuromuscular compromise needs immediate Orthopedic consultation. These are all rare in small children fortunately.


References
Shrader MW. Proximal humerus and humeral shaft fractures in children. Hand Clin 2007; 23:431.
Hohloch L, Eberbach H, Wagner FC, et al. Age- and severity-adjusted treatment of proximal humerus fractures in children and adolescents – A systematical review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2017; 12:e0183157.
Benoudina S, Humeral surgical neck fracture. Case study, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 24 Mar 2023) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-23972








